Demold rubber product is one of the critical stages in the rubber molding process. This step is crucial because it directly impacts the quality and integrity of the final rubber product. However, many rubber product manufacturers produce molded products, and the difficulty of demold the mold has become a frequent problem. In this post, we will explore why is it difficult to release the mold, and how to prevent the problem difficulty of demolding rubber products.
Why Is It Difficult to Demold Rubber Product?
Demolding rubber products can be challenging due to several factors that affect the ease with which the molded product can be released from the mold. Here are the main reasons:
1. Adhesion Issues
Rubber compounds often stick to the mold due to their strong adhesive properties, especially in tire manufacturing. Ineffective or improperly released agents will exacerbate this issue.
2. Mold Design and Condition
Small draft angles, intricate mold shapes, and rough or damaged mold surfaces complicate the demolding process. Regular maintenance and appropriate surface treatments are crucial.
3. Environmental Factors
Temperature and humidity variations, along with improper storage of rubber materials, impact rubber properties, and the demolding process.
4. Material Properties
Different rubber compounds, additives, and fillers affect shrinkage, elasticity, and adhesion, influencing the ease of demolding. High shrinkage rates cause a tighter grip on the mold.
5. Process Parameters
Inconsistent curing times, temperatures, and variations in injection pressure (high injection pressure) and speed can lead to increased adhesion, making demolding difficult.
6. Release Agent Application
The method, frequency, and type of release agent application significantly impact demolding. Inconsistent application and unsuitable release agents can lead to increased adhesion issues.
Defects in Rubber Products Caused by Poor Demolding
Poor demolding of rubber products can lead to several defects that compromise the quality and functionality of the final product. Here are some common defects caused by inadequate demolding processes:
1. Tearing (Tear Loss):
This occurs when the rubber product tears during demolding, often due to excessive adhesion between the rubber and the mold or insufficient draft angles.
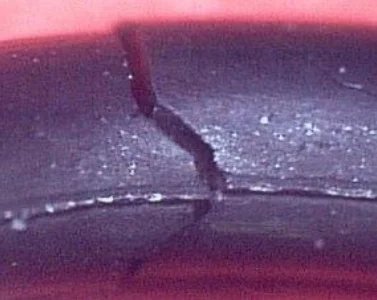
2. Deformation:
Improper demolding can cause the rubber product to deform, leading to parts that do not meet dimensional specifications or functional requirements.

3. Structural Rips:
Larger rips that penetrate deeper into the product can significantly weaken its structural integrity.

4. Sticky Mold:
When the molded material lacks internal release agents or the mold surface is rough, the rubber can stick to the mold, making demolding difficult and leaving irregular defective areas on the product.

5. Delamination:
Poor adhesion between layers of rubber or between rubber and other materials can cause layers to separate, compromising the structural integrity of the product.

How to Prevent Difficult Demold Rubber Product?
To prevent difficult demolding of rubber parts, here are some effective methods:
1. Optimize Mold Design
Adequate Draft Angles: Ensure that the mold design includes sufficient draft angles, typically between 1° and 3°, to facilitate easier release of the rubber product from the mold.
Simple and Smooth Mold Structure: Design molds with simple, smooth contours and avoid complex shapes that can trap the rubber. Regularly maintain and clean the mold to prevent surface roughness and deformation.
2. Use Appropriate Release Agents
Internal Release Agents: Incorporate internal release agents into the rubber compound to reduce adhesion to the mold. This can decrease the need for external release agents and prevent contamination of the mold surface.
External Release Agents: Apply suitable external release agents, such as silicone-based or water-based agents, to the mold surface. Ensure even and consistent application to avoid areas where the rubber might stick.
3. Control Process Parameters
Proper Injection Pressure and Speed: Optimize injection pressure and speed to prevent excessive force that can cause the rubber to adhere tightly to the mold. High injection pressure can lead to elastic deformation of mold parts, making demolding more difficult.
Ensure Proper Vulcanization Time and Temperature: Ensure proper vulcanization by controlling the curing time and temperature. Inadequate curing can result in incomplete vulcanization, while excessive curing can cause scorching and surface defects.
4. Use Appropriate Material Formulations
Adjust Rubber Compound: Modify the rubber compound formulation to include appropriate levels of vulcanizing agents and accelerators. This helps achieve optimal curing and reduces the likelihood of adhesion issues.
Use Proper Additives and Fillers: Use additives such as carbon black to enhance the rubber’s properties and improve demolding. Ensure that the formulation is balanced to prevent excessive adhesion.
5. Regular Mold Maintenance and Treatment
Regular Cleaning and Maintenance: Keep the mold clean and well-maintained to prevent buildup of residues that can increase adhesion. Techniques such as plating, Teflon spraying, and sandblasting can help maintain a smooth mold surface.
Surface Treatments: Apply surface treatments like clear acrylic lacquer to the mold to create a barrier that reduces adhesion. Ensure the treatment is compatible with the rubber material being used.
6. Improve Demolding Techniques
Automated Demolding: Use automated demolding systems such as ejector pins, air ejection, and robotic handling to ensure consistent and efficient release of rubber products from the mold.
Manual Techniques: Train workers in proper demolding techniques to minimize damage to rubber products and ensure a smooth release.
Conclusion
Demolding rubber product is a crucial manufacturing step that affects product quality and efficiency. However demold rubber products can be challenging due to rubber’s properties. The manufacturer can implement strategies like optimizing mold design, using suitable release agents, and maintaining proper process parameters to prevent demolding issues.






